- Home
- Hearing Loss
- Audiology
What is Noise-Induced Hearing Loss?
2020-11-05 Most of the sounds that we encounter in our day-to-day lives are at safe levels and will not damage our hearing. However, excessively loud sounds can be harmful to our ears, even when exposed for a short period of time. The saying “it's so quiet, you can hear a pin drop” is a real goal for the more than 10 million Americans that have irreversible hearing loss due to noise exposure.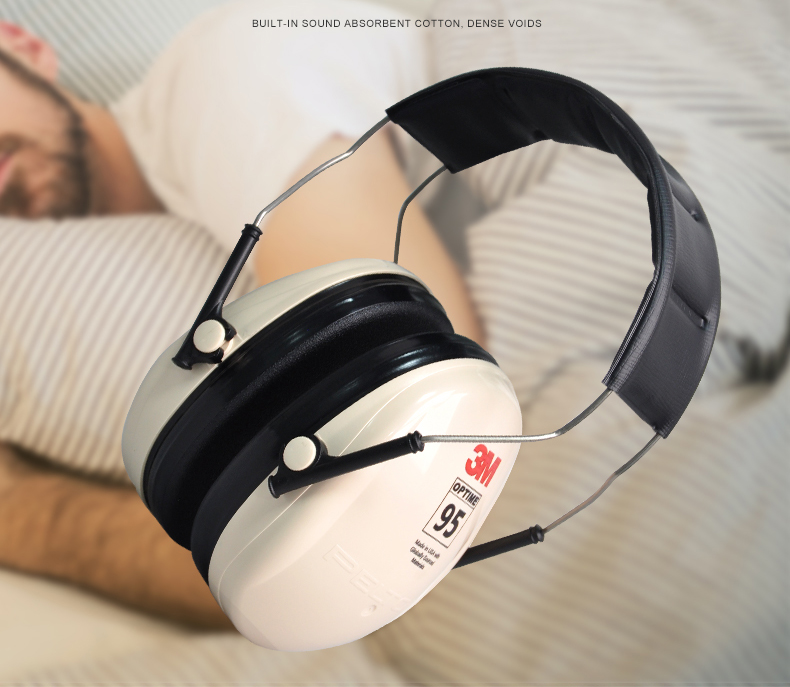
Noise-induced hearing loss is hearing loss resulting from exposure to loud sounds. This can be a sudden intense “impact” sound or exposure to loud noise over an extended period of time. Noise-induced hearing loss can be immediate, or it can occur gradually over time, getting worse as you get older. It can occur in both ears, one ear and can be temporary or permanent.
Causes of noise-induced hearing loss
We measure sound in a unit known as decibels (dB). Normal conversational speech is usually between 50dB and 60dB - sounds louder than 85 dB can cause hearing loss. The louder the sound, the shorter amount of time of exposure before a hearing loss results. You have a greater chance of suffering from noise-induced hearing loss if you are in an environment with extreme noises for any extended time. Examples include:
* Gunfire
* Explosives
* Machinery/power tools
* Jet engines
* Lawn equipment
* Emergency vehicles/alarms
* Concerts
* Musical instruments
* Personal music players
* Sporting events
* Motorcycles/heavy traffic

Symptoms of noise-induced hearing loss
When you are exposed to loud sounds over many years, hearing loss is usually very gradual and can be hard to detect until it becomes more pronounced. Symptoms will be similar to what you would experience with other types of hearing loss, including difficulty understanding speech, especially in noisy environments, and muffled or distorted hearing.
Exposure to a loud “impulse” noise such as an explosive or gunfire at close range can cause immediate damage (also known as acoustic trauma). The damage may be temporary or, if intense enough, can be permanent. It is also possible for the eardrum to rupture from this impulse noise.
Tinnitus – the perception of sound such as ringing, buzzing, hissing, pulsing in the absence of outside stimulus - is another symptom of noise-induced hearing loss. Again, this may be temporary or permanent, and in one or both ears.
Treatment and prevention of noise-induced hearing loss
The good news is noise induced hearing loss is completely preventable. If you understand the hazards of noise and how to protect your hearing health, you can protect your hearing for life. Here are a few easy ways:
* Know the noises that can cause damage (85 dB or above)
* Wear earplugs or other protective devices when doing activities where you will be exposed to loud noise (earplugs and earmuffs are widely available at hardware and sporting goods stores)
* Be alert to hazardous noises in the environment
* Protect the ears of children

If you’re concerned you or someone you know is suffering from noise-induced hearing loss, schedule an appointment with a hearing healthcare professional in your area. Hearing loss doesn’t have to be debilitating, find the best treatment for you today!
Latest
Audiology











All 0 comments