- Home
- Hearing Loss
- Audiology
Hearing loss may cause Alzheimer's?
2021-06-25With the social and economic growth and the continuous improvement of medical conditions, my country has entered an aging society, and the elderly are a high incidence of cognitive dysfunction. Mckhann et al. first linked hearing loss with cognitive function when studying mental illness. In recent years, hearing loss and Alzheimer's have a close relationship, which has been understood by more and more people.
Effects of hearing loss on cognitive development. According to WHO data, the prevalence of Alzheimer’s disease for elderly people with mild, moderate, and severe hearing loss is 2 times, 3 times, and 5 times that of the elderly with normal hearing; each increase of one standard deviation of hearing loss will increase 0.23% of dementia manifestations.
What is Alzheimer's?
Alzheimer disease (AD), also known as senile dementia, is a degenerative disease of the central nervous system, with an insidious onset and a chronic and progressive course. Mainly manifested as neuropsychiatric symptoms such as progressive memory impairment, cognitive dysfunction, personality change and language impairment, which seriously affect social, professional and life functions.
What is the relationship between hearing loss and Alzheimer's? Can alzheimer's cause hearing loss, is hearing loss a sign of dementia?
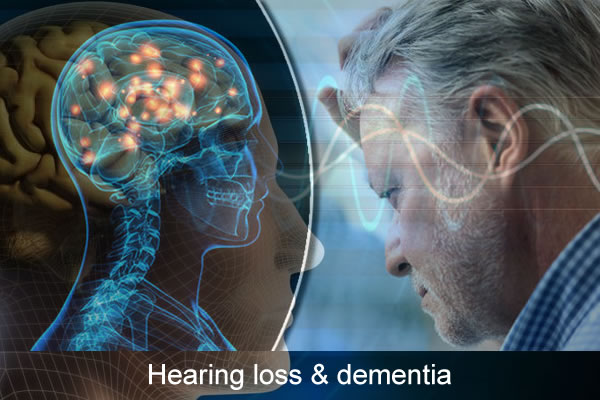
First, let's see how we hear the sound.
Sound is collected through the auricle and transmitted to the inner ear through the middle ear of the outer ear. The cochlea of the inner ear senses the sound and transforms it into nerve impulses that are transmitted to the auditory center of the cerebral cortex through the auditory nerve, and are connected with the language center to finally understand the meaning of speech. How does hearing loss affect the body?
However, when hearing declines, the auditory pathway is inhibited, and the brain's input (stimulus) is significantly reduced. This may greatly reduce the available resources of the language center to process sound, and affect the speech recognition ability of patients with hearing loss.
Side effects of hearing loss
While hearing loss directly affects the auditory center and language center, it also affects other areas of the brain. Due to hearing loss, the auditory center of our brain cannot be effectively stimulated, and the brain will allocate the functions of other regions to the auditory center, which causes the stimulation of other regions to be reduced, thereby increasing the overall load of the brain. Therefore, hearing loss is an important factor in inducing Alzheimer's disease.
Some scholars believe that hearing impairment can be used as a factor that promotes the occurrence of senile dementia, that is, the more severe the hearing impairment, the more severe the cognitive impairment.

Early intervention for hearing loss
The curative effect of early treatment of any disease is better than late treatment, and Alzheimer's is no exception.
Studies have shown that the use of hearing aids in the elderly can effectively avoid cognitive decline. After wearing hearing aids, the continuous listening ability is ensured, so that the centers of the cerebral cortex can maintain effective activity and slow down the occurrence of Alzheimer's disease. Rechargeable bte hearing aids or rechargeable CIC hearing aids are usually ideal for the elderly, eliminating the hassle of frequent battery replacement.
Of course, in addition to hearing intervention and improvement of hearing, maintaining an optimistic attitude, healthy eating, and strengthening exercise all have a certain effect on preventing Alzheimer's disease.
Latest
Audiology











All 0 comments