4 main causes of hearing loss
To treat and prevent hearing loss, it is also necessary to understand the factors that cause hearing loss in daily life, early detection and early treatment. There are four common causes of hearing loss, and these four must be paid attention to.

1. Ear diseases
Hearing loss may be caused by ear diseases, such as otitis externa, foreign body in the outer ear, etc. Sometimes acute and chronic middle ear problems can cause hearing loss and tinnitus. If you have ear diseases, it is best to go to a regular hospital for relevant examinations and receive treatment. Don't delay, otherwise it will develop in a bad direction.
2. Hearing loss caused by noise
Many users have nervous tinnitus, which is because the ears hear some noise for a long time, or the living environment is relatively noisy. Long-term exposure to noise will greatly reduce the function of our inner ear, so we avoid being in such an environment, we can wear earmuffs, earplugs, etc. to buffer some noise and reduce the negative impact of noise.
3. Bad living habits
How important it is to develop good living habits can keep us in a healthy state and full of vitality. For example, long-term drinking, drinking coffee, etc. Excessive intake of alcohol and caffeine will aggravate the symptoms of nervous tinnitus, resulting in hearing loss. In addition, smoking can cause blood oxygen to drop, and heavy smokers generally have symptoms of tinnitus. Therefore, if you want to get rid of tinnitus and hearing loss, you must start with developing good living habits.
4. Hearing loss caused by excessive stress
Excessive stress may lead to hearing loss. This is real. Nowadays, social pressure is increasing, which leads to decreased immunity, disordered endocrine system, and hearing loss caused by insufficient brain congestion.
This article can basically solve for you: causes of hearing loss, medical causes of hearing loss, how is hearing loss caused? What can cause hearing loss? What are the main causes of hearing loss? And so on. If you need help, please contact us.
Tip: Wearing hearing aids is one of the best ways to deal with hearing loss. Austar - A leading manufacturer and supplier of hearing aids in China.

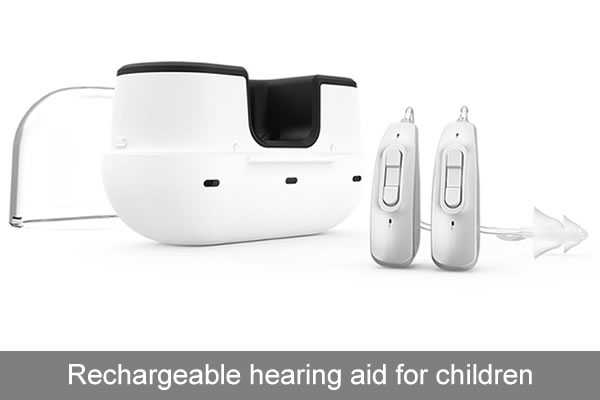
How to check your child's hearing aid every day?
Hearing aids are electronic devices, but sometimes they are damaged. Every day, children rely on their parents to check whether the hearing aids are safe and functioning properly. The earlier problems are found, the faster they can be solved. For example, charging at night, rechargeable bte hearing aids used during the day. Need to check whether the child forgets to charge before going to bed.
This is the way to keep your child's hearing aids in the best condition:

Get the right tools
When the child is fitting the hearing aid for the first time, the store should provide or ask the parents to prepare the hearing aid Maintenance Kit by themselves, and ask the audiologist to demonstrate how to operate. The tools in the maintenance kit include: simple monitoring earplug / ear mold, measuring appliance, drying box, earwax brush, blowing balloon, etc. If you have any questions or need to learn how to use it again, please feel free to ask your audiologist.
Quick check
Morning is often one of the busiest time for everyone, so the minimum requirement is the following quick check.
- Turn on the hearing aid, hold it in your hand and listen to see if there is a whine. If yes, it means that the hearing aids are working now; If you don't hear it, please check the battery or ear mold for earwax blockage, broken sound pipe, etc.
- Simple safety check. For example, whether the safety lock is locked or whether the ear hook and acoustic catheter are connected normally.
Children's language awareness test

If the child is old enough to participate, the child voice detection test or Lin's six tone test can be conducted in the morning, which is another good choice. It checks the child's hearing and hearing aids at the same time. If you have any questions about your child's hearing, or if they plan to do something that focuses on listening, such as language lessons or speech therapy, they can do it repeatedly during the day.
- Choose a quiet room.
- When you stand one meter behind the child, please make a sound at the normal voice volume, send out randomly at a time, and Pause briefly for the child's response.
- Once the child confirms or repeats the sound, please change to the next sound.
- Step back, about two to four meters from the child, and then repeat the exercise to see how distance affects their listening.
- The sound, a child hears with a hearing aid depends on the type and extent of hearing loss. Please contact your audiologist to find out what your child should be able to hear at different distances.
Other tips
- Use of drying hearing aid tools: storing the hearing aid in a drying box can make the hearing aid dry, thus reducing the number of maintenance. This is especially important in humid environments or when children sweat more.
- Encourage independence: if the hearing aid doesn't work, please observe the child's reaction, ask the child to tell you if there is any abnormality, and gradually let them participate in taking care of their hearing aid.
- Keep dry: unless you have a special waterproof hearing aid, remove the aid before bathing or swimming.
- Remove the hearing aid before going to bed: it's a comfort consideration. Even if the child is open when sleeping, if it is just a nap, it can not be removed, so it is not afraid to disturb them.
It's important to check your child's hearing aids every day. You need to do this until your child is old enough to tell you when something is wrong. If you have any questions or want to order cleaning accessories, please contact your fitter or manufacturer.
About AUSTAR Hearing Aids
AUSTAR is a professional hearing aid manufacturer for medical standards in China, wholesale behind-the-ear (BTE) and in-the-ear (ITE) types of hearing aids, rechargeable hearing aid. Digital programmable hearing aids use our own fitting system software for programming hearing aids to ensure superior quality of hearing aid and make price competitive in this industry. Our main customers are hearing aid wholesalers/dealers across the USA, Europe, Asia and Mid East.
Please feel free to contact us if you are hearing aid wholesalers/ distributors and looking for a trustworthy Chinese manufacturer/ supplier. No only provide a full range of hearing aids, we have a strong R&D teams and engineers to support your any special requirement and development. We are not only your supplier, but also your partner and technical supporter. AUSTAR commit to provide customers with excellent service, satisfactory quality and competitive prices, help you expand your market and save hearing aid price/ costs!

How to maintain hearing aids in summer?
Summer Hearing Aid Care Tips
The weather is getting warmer and summer is coming. Are you ready with your hearing aid?
In summer, the climate is hot and humid with more precipitation and high air humidity; In addition, the human body is more likely to sweat, hearing aids are also vulnerable to moisture erosion. Therefore, the most important thing for hearing aid maintenance in summer is to take moisture-proof and waterproof measures.
Guide for Summer Hearing Aid Care
1.Routine maintenance.
Wash your face, hair and bath. Don't wear it immediately after washing. Wear it after ear canal and auricle are wiped clean.
2.Sweat protection.
High temperature in summer makes people sweat a lot, which may corrode hearing aids and affect the performance and life of hearing aids. Therefore, after using the hearing aid every day, clean the sweat on the surface of the hearing aid with a dry soft cloth, and then place it in the hearing aid drying box regularly for drying.
3.Rainwater protection.
In summer, there is a lot of precipitation, so it is better not to wear hearing aids or do a good job of rainproof on rainy days. Return to the room and dry the hearing aid in time.
4.Cerumen protection.
Summer ear secretion will also increase, for customized ITE hearing aids, to check whether there is earwax or impurities blocking cerumen baffle. If this happens, please clean or replace the baffle with a small brush. For behind the ear hearing aids, if the sound guide tube is blocked by earwax or impurities, please clean it immediately.

5.Swimming protection.
Swimming is a good summer activity. Before any water sports, you should take off the hearing aid and keep it properly. For swimming without hearing aid, please always swim with others to avoid missing the relevant warning and lifeguard's voice and ensure safety. If the hearing aid has been flooded, such as swimming in the sea, you should also pay attention to the protection of sand, to avoid sand dust into the hearing aid.

6.Sunshine protection.
Outdoor sunscreen is very important in summer. Avoid applying to the hearing aids when applying sunscreen lotion. When using sunscreen spray, be careful not to spray on hearing aids to prevent hearing blockage or other injuries. Wipe with a dry soft cloth after daily use.

7.Condensate protection.
Wearing hearing aids frequently in and out of cold and hot alternating environment, hearing aids are prone to produce condensate. In summer, we often go in and out of the hot outdoor and cool air-conditioned room, so it is very easy to make the hearing aids produce condensate. If there is condensed water, take off the sound guide tube of the ear back machine, dry the water drops, and then place the hearing aid in the drying box for drying.
Summer heat, summer protection, help to delay the service life of hearing aids, improve the listening experience.
About AUSTAR Hearing Aids
AUSTAR is a professional hearing aid manufacturer for medical standards in China, wholesale behind-the-ear (BTE) and in-the-ear (ITE) types of hearing aids, rechargeable hearing aid. Digital programmable hearing aids use our own fitting system software for programming hearing aids to ensure superior quality of hearing aid and make price competitive in this industry. Our main customers are hearing aid wholesalers/dealers across the USA, Europe, Asia and Mid East.
Please feel free to contact us if you are hearing aid wholesalers/ distributors and looking for a trustworthy Chinese manufacturer/ supplier. No only provide a full range of hearing aids, we have a strong R&D teams and engineers to support your any special requirement and development. We are not only your supplier, but also your partner and technical supporter. AUSTAR commit to provide customers with excellent service, satisfactory quality and competitive prices, help you expand your market and save hearing aid price/ costs!
Why is it still hard to hear with the most expensive hearing aid?
Is the more expensive hearing aid on the market, the better? In fitting work, we will hear complaints from some users, such as “I can't hear clearly when I am equipped with one of the most advanced and expensive hearing aids or brands”, “I can't hear clearly when I have spent so much on hearing aids” and so on.
A hearing aid is a device designed to improve hearing by making sound audible to a person with hearing loss. Hearing aids are classified as medical devices in most countries, and regulated by the respective regulations. Small audio amplifiers such as PSAPs or other plain sound reinforcing systems cannot be sold as "hearing aids".
Hearing aid brands and prices
Will products at different prices affect the sound quality of hearing aids? The answer must be yes.

The more expensive the hearing aid is, the richer its functions are and the more advanced the technology is, so as to meet the higher listening needs. However, the price is not the only factor affecting the sound quality of hearing aid, and it is better to say that the suitable one for users is the best. Our latest mini rechargeable digital hearing aids are affordable and popular with hearing-impaired people. Let's look at the factors that affect the sound quality of hearing aids?
1. User's listening
The types of hearing loss, the degree of hearing loss and the direction of audiogram have certain influence on the listening effect. For example, if the user has no residual hearing, the better hearing aids can not achieve the effect.
2. Is the power of hearing aid appropriate
The power selection of hearing aids is very important. Too large or too small can affect the listening effect. For example, if the user's hearing loss reaches 100 dB, but the hearing aid with ordinary power is selected, then the amplified sound of the hearing aid can not meet the user's demand, so it is impossible to listen clearly. Therefore, only when hearing aids of suitable power are selected, can we hear comfortably and clearly. If your hearing loss is less than 70dB and you like the type of hearing aid in the ear, then the rechargeable cic hearing aid is very suitable for you.
3. Binaural selection
If both ears have hearing loss, hearing aids are recommended. If both ears have hearing loss and only one ear is worn, it is easy to cause asymmetry of hearing threshold of both ears, resulting in loss of sense of direction and balance, and the ear that is not worn is prone to hearing deprivation
4. Speech recognition rate of users
The speech recognition rate affects the user's speech listening ability, which determines whether the user can understand the speech. If the user's speech recognition rate is low, no matter how light the hearing loss is, no matter how expensive the hearing aid is, the user may only hear the voice, and cannot understand the meaning of the voice
5. Level of Hearing Fitting Engineer
There is a saying in the listening industry that 30% of the effectiveness of hearing aids is determined by hearing aids, and the remaining 70% is determined by the fitting engineer. Therefore, in the selection of hearing aids, we must go to a professional fitting center and find a qualified fitting specialist for fitting.

There are many factors that affect whether hearing aids can hear clearly. Hearing aids can help hearing impaired patients to listen by amplifying and processing the sound, but there is no way to replace our own cochlea and auditory system to analyze and identify the sound, which is impossible to achieve the effect of normal ears. Therefore, we should have reasonable expectations before fitting. Gradually adapt to the initial discomfort of wearing, actively practice, make hearing aids become practical and effective, become a good helper in life and work.
AUSTAR is a leading manufacturer of hearing aids in China, specialized in research and development, production and sales of hearing aids and hearing equipments.
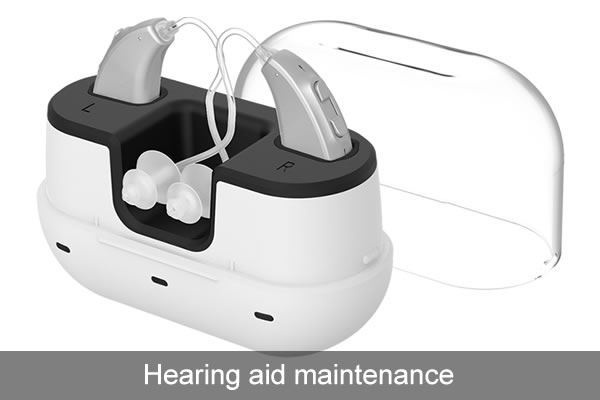

Hearing aid maintenance
Information about hearing aid maintenance, how to clean the hearing aid microphone, etc.
Hearing aids require special attention to ensure their proper functioning. You should have special cleaning tools for hearing aids and drying tanks provided by hearing aid companies. If so, please use it every night. Rechargeable BTE hearing aids and ITC hearing aids also require maintenance. If you need to replace parts or purchase consumables, please contact your audiologist to confirm whether these consumables can be shipped to your home. Remember these tips to keep your hearing aids in good working order.
Perform visual inspections every day. Start from the part that directly enters the ear, and take a closer look at the entire hearing aid body. Check whether the earwax may prevent the sound from entering normally. The hearing aid body or tube should also be checked for cracks.

If you are using custom-made hearing aid, check the cerumen cap-if you see a lot of earwax, this is a good time to replace it!
If you are using a open-fit hearing aid, please check whether there is earwax on the earplugs of the hearing aid. If there is a large amount of earwax, please find out how to clean or replace it from the user manual. Please check whether the sound tube is broken or needs to be replaced. If it is a thin tube back-to-ear machine (BTE-OE), please also remove the earplugs and clean the sound tube. You can use fishing line to clean it.
Check the battery. Hearing aid batteries should be kept for at least 5 to 10 days, depending on the hearing aid model, battery size and the use of the connectivity function (Bluetooth). If you have a battery tester at home, please check whether the battery is sufficient to make the hearing aid work with the best performance; if you do not have a battery tester, it is recommended that you record the battery usage time. And make sure to do the following:
Please carry spare batteries with you and store them in a cool and dry place (not the refrigerator)
For rechargeable hearing aids: such as rechargeable cic hearing aids. Please reserve enough recommended charging time to enable the hearing aid to be fully charged. If necessary, you can check the relevant instructions in the user manual. Record the length of time the hearing aid has been used. If you find that the charging status is not as expected, please contact your optician.
Please clean the hearing aid regularly with a soft dry cloth. Please check hearing aids, earmolds, earplugs or pipes for dirt and earwax.
For users of hearing aids using customized ear molds, please note that they can be removed from the hearing aids, cleaned with warm (rather than hot) soapy water, and then washed clean. Make sure the earmould is dry before re fitting it to the hearing aid.
Circular earplugs used with open-fit hearing aids should be cleaned with dry cloth or special tools provided by the fitting engineer. Some fitters will provide replacement earplug spare parts. If your earplug is discolored, broken or damaged, please remove it and replace it with a new one and connect it to the hearing aid.
Minimize moisture in hearing aids. The drying equipment (drying box) can prevent moisture from accumulating inside the hearing aid and prolong its service life. Please remove the battery before putting the hearing aid into the storage container. If you live in a very humid area, please ask your fitter if you use proper drying equipment for your hearing aid. If a simple jar or dryer is not enough, a more advanced dryer can be used.

Can hearing aids reduce tinnitus?
Reading this article will help you answer related questions such as hearing aid for tinnitus masking, can hearing aids make tinnitus worse and hearing aid for tinnitus cost.
Tinnitus is not a disease, but a symptom of persistent hearing of disturbing calls.
The cause of tinnitus?
At present, there is no exact evidence to prove why tinnitus occurs, and there is no completely objective examination that can directly reflect the cause of tinnitus. At present, it is speculated that tinnitus may be caused by physiological phenomena, such as acoustic neuroma, nasopharyngeal carcinoma, etc; It may also be accompanied by hearing changes, such as sudden deafness (hearing loss); Other reasons may also be due to sleep, diet and so on.

The majority of tinnitus patients are associated with long-term hearing loss or sudden deafness (hearing loss). It is generally believed that hearing loss will reduce the stimulation of sound to the brain, and then cause changes in the brain's processing of sound. Tinnitus is the product of these abnormal brain discharges of sound.
How can hearing aids relieve tinnitus?
According to a survey in 2007, about 60% of tinnitus patients feel relieved when wearing hearing aids, while 22% of them feel significantly improved. When tinnitus and hearing loss coexist, most patients can feel relieved by using hearing aids.
Hearing aids can amplify sound and increase the stimulation of subtle environmental sound to the brain auditory system. Under the long-term sound stimulation, we hope to slow down the abnormal discharge of the brain to sound. And most of the hearing aids now have the function of tinnitus masking. There are different tinnitus masking sounds that can slow down tinnitus or distract attention. Of course, it won't have an immediate effect. It also needs a period of stimulation to slow down the symptoms and influence of tinnitus. Our rechargeable BTE hearing aids and rechargeable CIC hearing aids have such a tinnitus masking effect.
Hearing aids not only increase the ambient sound, but also cover the patients' perception of tinnitus, so as to reduce the physiological and psychological impact of tinnitus on patients.
In addition to the common hearing loss will be accompanied by tinnitus, there are many reasons closely related to tinnitus, when tinnitus has an impact on life, we should actively look for hearing professionals for relevant consultation, in order to eliminate the relevant risk factors and deal with it as soon as possible!
Hearing loss may cause Alzheimer's?
With the social and economic growth and the continuous improvement of medical conditions, my country has entered an aging society, and the elderly are a high incidence of cognitive dysfunction. Mckhann et al. first linked hearing loss with cognitive function when studying mental illness. In recent years, hearing loss and Alzheimer's have a close relationship, which has been understood by more and more people.
Effects of hearing loss on cognitive development. According to WHO data, the prevalence of Alzheimer’s disease for elderly people with mild, moderate, and severe hearing loss is 2 times, 3 times, and 5 times that of the elderly with normal hearing; each increase of one standard deviation of hearing loss will increase 0.23% of dementia manifestations.
What is Alzheimer's?
Alzheimer disease (AD), also known as senile dementia, is a degenerative disease of the central nervous system, with an insidious onset and a chronic and progressive course. Mainly manifested as neuropsychiatric symptoms such as progressive memory impairment, cognitive dysfunction, personality change and language impairment, which seriously affect social, professional and life functions.
What is the relationship between hearing loss and Alzheimer's? Can alzheimer's cause hearing loss, is hearing loss a sign of dementia?

First, let's see how we hear the sound.
Sound is collected through the auricle and transmitted to the inner ear through the middle ear of the outer ear. The cochlea of the inner ear senses the sound and transforms it into nerve impulses that are transmitted to the auditory center of the cerebral cortex through the auditory nerve, and are connected with the language center to finally understand the meaning of speech. How does hearing loss affect the body?
However, when hearing declines, the auditory pathway is inhibited, and the brain's input (stimulus) is significantly reduced. This may greatly reduce the available resources of the language center to process sound, and affect the speech recognition ability of patients with hearing loss.
Side effects of hearing loss
While hearing loss directly affects the auditory center and language center, it also affects other areas of the brain. Due to hearing loss, the auditory center of our brain cannot be effectively stimulated, and the brain will allocate the functions of other regions to the auditory center, which causes the stimulation of other regions to be reduced, thereby increasing the overall load of the brain. Therefore, hearing loss is an important factor in inducing Alzheimer's disease.
Some scholars believe that hearing impairment can be used as a factor that promotes the occurrence of senile dementia, that is, the more severe the hearing impairment, the more severe the cognitive impairment.

Early intervention for hearing loss
The curative effect of early treatment of any disease is better than late treatment, and Alzheimer's is no exception.
Studies have shown that the use of hearing aids in the elderly can effectively avoid cognitive decline. After wearing hearing aids, the continuous listening ability is ensured, so that the centers of the cerebral cortex can maintain effective activity and slow down the occurrence of Alzheimer's disease. Rechargeable bte hearing aids or rechargeable CIC hearing aids are usually ideal for the elderly, eliminating the hassle of frequent battery replacement.
Of course, in addition to hearing intervention and improvement of hearing, maintaining an optimistic attitude, healthy eating, and strengthening exercise all have a certain effect on preventing Alzheimer's disease.
What should the family members of hearing loss patients pay attention to?
Communicating with People with Hearing Loss, If you are speaking with someone who has a hearing impairment what should you do? Hearing loss not only affects patients' listening and communication, but also affects their lives, psychologically, and emotionally, so our family needs to give them more patience and care.

Communication
- Both parties should talk face-to-face, preferably within 3 meters;
- Keep the sound intensity moderate, speak as clearly as possible, and avoid shouting;
- The speech speed remains stable. If the hearing impaired person cannot hear clearly, the speech speed can be reduced appropriately, not too fast;
- Avoid talking in a noisy environment;
- Attract the attention of the hearing-impaired before speaking, and notify the hearing-impaired before changing the topic;
- Family members do not cover mouth shapes or facial expressions during communication, so that hearing-impaired people can better obtain information;
- The speaker should try to use short and clear sentences, and try to simplify the complicated sentences as much as possible;
- When the hearing-impaired person does not hear clearly, you can change to another more concise and easy-to-understand expression.
Psychological
Although hearing-impaired people with the help of hearing aids or cochlear implants, these two are only auxiliary tools after all and cannot restore the wearer's normal hearing. What the hearing-impaired people need most is to be accepted and understood by others.

- Family members should give more positive and positive feedback to the hearing-impaired, and encourage them to listen and talk more;
-
When communication is not smooth, family members need to be more patient and not show impatience. Otherwise, it will be easier for the hearing-impaired to use hearing aids.
Maintenance
For hearing-impaired people, especially children or the elderly, they may not be able to maintain their hearing aids well, or they may not be able to make a good judgment when a hearing aid fails. As family members, we need to always pay attention to the condition of their hearing aids and help clean and maintain them on time. To ensure that the hearing aid always provides the best hearing aid. It is recommended to use a rechargeable BTE hearing aid, or a rechargeable CIC hearing aid, to save the trouble of replacing the battery.

Hearing and hearing aid effects
Hearing-impaired people sometimes cannot find that their hearing conditions and hearing aid effects have changed, or find that they have not expressed them. At this time, we need our family to pay more attention and judge by some small daily details. For example, wearing hearing aids only needs to be normal before. It can be heard at the volume, but now it needs a louder sound or it needs to be repeated many times to hear clearly, then the hearing of the hearing-impaired person or the hearing aid effect of the hearing aid may have changed, then the family needs to help the patient make an appointment with audiologists, re-evaluate their hearing or adjust hearing aid parameters in order to achieve the best hearing aid effect.
As family members, it is necessary for us to understand the deafness and mental state of the hearing-impaired, master the correct communication methods, the correct way to use hearing aids, and maintain love and patience in communicating with the hearing-impaired. Patience and participation of family members will help increase the confidence of hearing-impaired people in using hearing aids and the effectiveness of hearing aids.
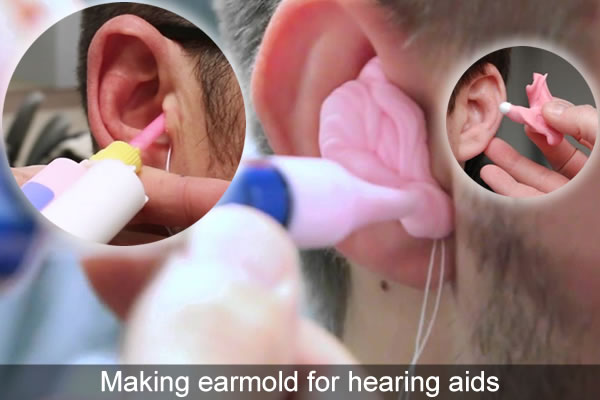
How to make an earmold/ear impressions for hearing aids
Making ear impressions for hearing aids is one of the important steps in the fitting process of hearing aids. Whether the ear impressions are made correctly is related to the hearing aid effects. For example, if the ear impressions are too large, the patient may feel swollen and painful when wearing the hearing aids; Too small will cause howling problems. In addition, making ear impressions is also the most dangerous step in hearing aid fitting. If you are not careful, it may be difficult to take out the ear impressions. The preparation of ear impressions is very important. The steps and precautions for the preparation of ear impressions are listed below.

Hearing aid earmold making guide
Before making ear impressions, prepare the tools one by one, and perform alcohol sterilization on the making tools such as tweezers for the search light.
Ask for medical history
Ask the patient whether he has had ear infections, surgery, etc. in the last 3 months. In particular, some patients undergoing radical mastoidectomy will have surgical cavities, which can be filled more when filling the cotton barrier, so that the patient's surgical cavities can be filled to avoid difficulties in removal.
Check the external ear canal
First check whether the external auditory canal is red and swollen; whether the eardrum is intact; whether there is pus or inflammation; whether there is ear wax blocked and need to take it out. For inflammation and pus, let the patient seek medical treatment first, and wait until it stabilizes, and then,take an ear impression. Then check the size, curvature and direction of the ear canal to determine where to place the ear barrier.
Place a cotton barrier
First, put the cotton barrier at the mouth of the ear canal, and then slowly push the center of the cotton barrier with the head of the ear probe to push the barrier flat across the second bend of the ear canal by 2-3mm (The position of the cotton barrier can be placed according to the type of hearing aid to be made. Slightly adjusted).
Ear impression materials are mixed
The matrix of the ear impression material and the coagulant are kneaded in a one-to-one ratio in the shortest possible time, knead it into a ball, put it into the syringe as soon as possible, and push it to the tip of the syringe with the syringe core to eliminate air bubbles and extrude the front Discard the impression material about 0.5 cm long and start the injection again. For some patients with dry ear skin, especially the elderly, you can apply some baby moisturizer to the external auditory canal first to avoid damage to the external auditory canal when the ear impression is taken out.
Fill the ear canal
When injecting, always hold down the cotton barrier and pull the cord to avoid deepening into the external auditory canal due to injection pressure. The tip of the syringe is 0.5-1.0cm deep into the external ear canal (note that there is a little gap between it and the ear canal). During the injection process, the front end of the syringe must always be buried in the ear print material, so that the ear print material overflows, and the syringe is withdrawn thereafter. The injection in the ear canal needs to be light and slow; when it reaches the ear concha cavity, the injection needs to be completed quickly. After the injection is completed, do not press hard on the outside to avoid the model being too large.
Take out the ear impression
After injecting the ear impression material, you should always pay attention to the solidification of the ear impression, and lightly scratch the ear impression with your fingernail. The best time to take it out is when it can pop up quickly. It is necessary to gently pull the impression away from the auricle to allow air to enter the ear to prevent the patient's discomfort due to the negative pressure in the ear canal. Then first take out the triangular fossa area, then tighten the auricle, raise the impression slightly, move the ear impression back and forth, and gently rotate it upwards, forwards, and outwards to remove it smoothly. If you encounter flat and large curvature, you cannot use the forward and outward turning method, and you must use the method of gently lifting the lower end of the ear, pulling it gently, and stopping it.

Check the ear impression
Observe whether the whole ear impression is intact and has no defects, whether the surface is smooth without swelling, dents, cracks or bubbles; whether the external auditory canal opening, interscreen notch, and concha cavity are intact; whether the ear impression exceeds the second bend by 2-3mm; Whether the mold has complete helix casters. If there is any defect, take it again immediately and pay attention to the operation of the defective part.
Check the external ear canal
After taking it out, use an electric otoscope to carefully observe whether there is any residual material left in the ear. If there is redness and swelling, use hydrogen peroxide to wipe the ear canal. The purpose is to quickly eliminate inflammation (the pressure of injection and injection may cause redness and swelling of the ear canal). Instruct patients to take a bath or wash their hair these days, if the ear canal gets water, it should be wiped dry with a cotton swab in time to avoid inflammation.

Learn the truth about tinnitus to improve the quality of life
If you are one of the millions of people in the world who suffer from tinnitus, then you know that it affects everything from work to home and social life, and the constant sound in your ears can also cause stress and frustration.
Tinnitus is the perception of sound without actual sound. For many people, tinnitus is characterized by ringing, but it also sounds like whistling, buzzing, or hissing. Ringing or buzzing noise in one or both ears that may be constant or come and go, often associated with hearing loss. Ringing in ears can have causes that aren't due to underlying disease. Examples include exposure to loud sounds, whiplash, head injuries, too much ear wax, or medication side effects.The noise you hear when you have tinnitus isn't caused by an external sound, and other people usually can't hear it. Tinnitus is a common problem. It affects about 15% to 20% of people, and is especially common in older adults.

According to the American Tinnitus Association, there are millions of tinnitus patients in the United States. Since many people suffer from tinnitus, it is more important to distinguish facts from rumors. Knowing the truth about tinnitus can provide you with the best opportunity to effectively cope with and reduce symptoms, thereby improving your quality of life.

Tinnitus is a disease?
Tinnitus itself is not a disease, but a symptom caused by many underlying diseases. The harmful noise, nerve damage, vascular disease and even brain trauma are just some of the possible factors that cause tinnitus, and it can also cause tinnitus (and hearing loss) due to certain drug reactions. There is currently no "cure" for tinnitus, but there are treatments available that can reduce symptoms and make it easier for people to coexist with it.
As long as you change your eating habits, tinnitus will disappear?
Although some people think that certain additives and food ingredients (such as alcohol, sodium, caffeine) can aggravate tinnitus, they are usually not the underlying cause. A balanced diet and maintaining a healthy lifestyle (including exercise) are always important to overall health, but tinnitus needs to be dealt with separately, and these alone cannot “cure” tinnitus.
Only people with hearing loss have tinnitus?
People with hearing loss may have tinnitus, and it is highly correlated, but tinnitus may also occur without hearing loss. If you are exposed to very loud noises such as rock concerts or explosions, you may hear temporary tinnitus. Certain diseases or drug use can also cause tinnitus, so even you don’t have hearing loss, it is worth a hearing examination.
Everyone with tinnitus will eventually become deaf?
Tinnitus and hearing loss often exist at the same time, but their condition are self-existent. Having tinnitus does not mean that you have hearing loss. Even if you have hearing loss, it does not mean that you will be completely deaf. Hearing aids can compensate for hearing loss, and some models can even deal with tinnitus symptoms at the same time.
Hearing aids for tinnitus
The tinnitus masking technology of hearing aids can conceal the internal sound of tinnitus by adding special external noises, thereby solving hearing loss and tinnitus symptoms. This is the so-called “masking”. The progress of sound therapy has achieved great success. Other methods include meditation, stress management techniques, and changes in diet and exercise. You can consult an expert specializing in tinnitus treatment some method that suits you.
Can hearing aids help with my tinnitus? Amplification with hearing aids can bring relief to people experiencing tinnitus, as they may boost ambient sounds that can help take the focus off of tinnitus.